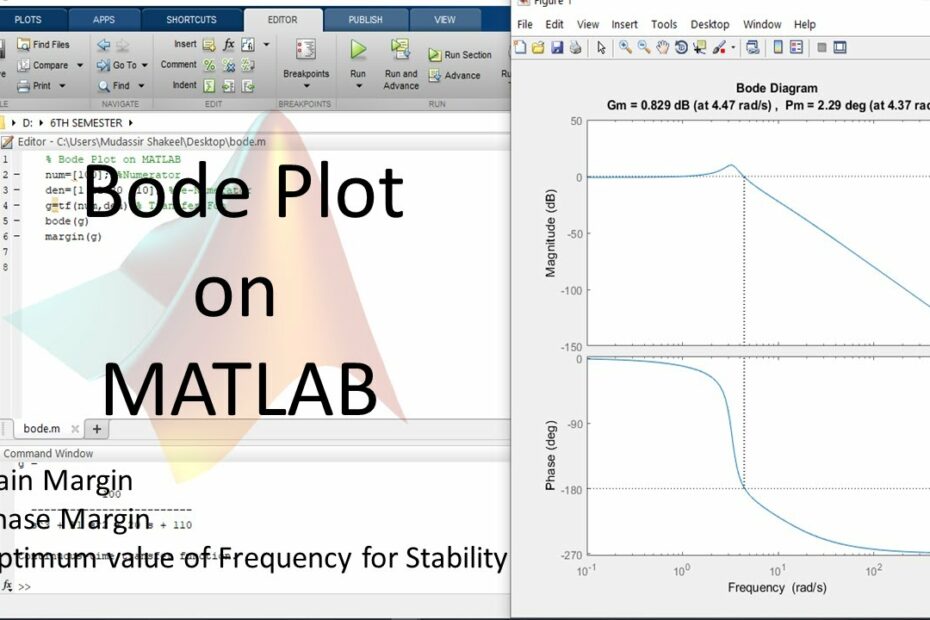
Let’s discuss the question: how to find gain margin in matlab. We summarize all relevant answers in section Q&A of website Achievetampabay.org in category: Blog Finance. See more related questions in the comments below.
How do you calculate margin gain in Matlab?
[ Gm , Pm , Wcg , Wcp ] = margin( sys ) returns the gain margin Gm in absolute units, the phase margin Pm , and the corresponding frequencies Wcg and Wcp , of sys . Wcg is the frequency where the gain margin is measured, which is a –180° phase crossing frequency.
How do you calculate gain margin?
The gain margin is defined as the reciprocal of the magnitude |G(jω)| at the frequency at which the phase angle is −180°. Defining the phase crossover frequency ω1 to be the frequency at which the phase angle of the open-loop transfer function equals −180° gives the gain margin Kg: K g = 1 | G ( j ω 1 ) | .
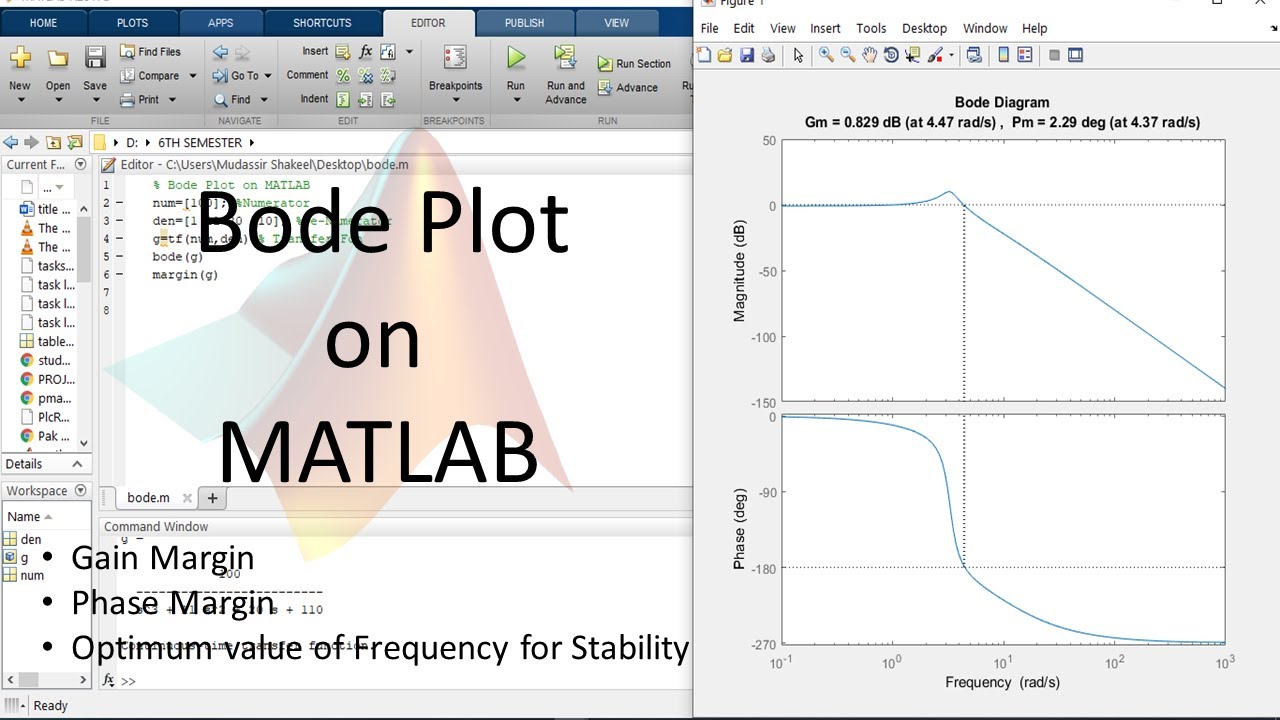
Bode Plot on MATLAB || Graph of frequency Response of system || Gain Margin \u0026 Phase Margin
Images related to the topicBode Plot on MATLAB || Graph of frequency Response of system || Gain Margin \u0026 Phase Margin

What is a gain margin?
Gain margin is defined as the amount of change in open-loop gain needed to make a closed-loop system unstable. The gain margin is the difference between 0 dB and the gain at the phase cross-over frequency that gives a phase of −180°.
How do you find the gain margin and phase margin of a root locus?
The gain margin will be given by the point where the root locus crosses the imaginary axis in the complex plane. The phase margin is associated with the place where the root locus has a magnitude of one, and the damping ratio is equivalent to the cosine of the angle of the poles.
How do you find the gain margin on a Bode plot?
It is usually expressed as a magnitude in dB. We can usually read the gain margin directly from the Bode plot (as shown in the diagram above). This is done by calculating the vertical distance between the magnitude curve (on the Bode magnitude plot) and the x-axis at the frequency where the Bode phase plot = 180°.
How do you calculate delay margin?
Multiply numerator and denominator by the complex conjugate of the denominator. = delay margin = time delay for the system to be on the verge of instability.
How do you solve a Bode problem?
- Bring the given G(s)H(s) transfer function into standard time constant form.
- Replace all s by jω to get the frequency domain transfer function.
- Make a table of the standard factors present in the given transfer function.
- Now analyze the table of factors.
How much gain margin is enough?
A gain margin of 10 dB is reasonable. This allows parameter changes which could cause the loop gain to change by a factor of approximately 3 before the system becomes unstable. The gain margin for the loop gain of Figure 2 is approximately 17 dB, a good value for a rugged and conservatively-designed control system.
Why is gain margin negative?
A positive gain margin means how much the control system gain can be increased, while a negative gain gain margin means how much the control system gain can be reduced. Therefore, in response to various uncertainties, the control system should satisfy negative and positive gain margin and phase margin.
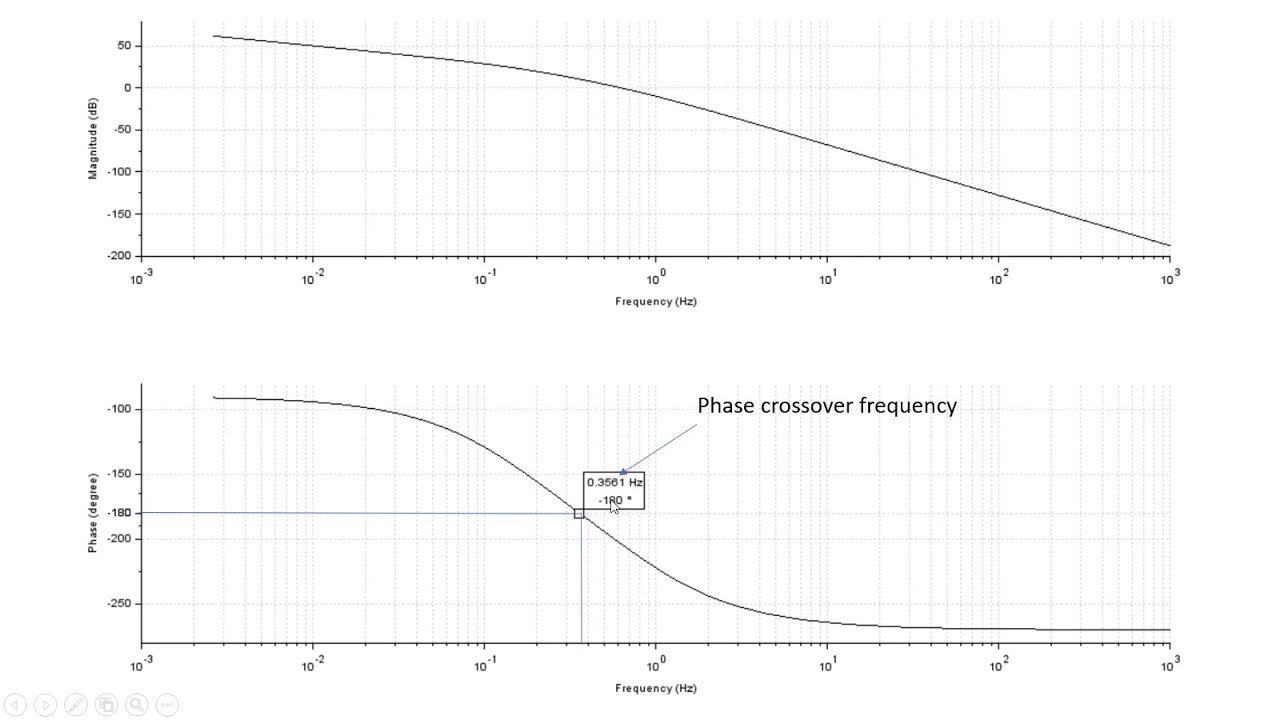
How to Calculate Gain and Phase Margin and Cross Over Frequencies From a Bode Plot
Images related to the topicHow to Calculate Gain and Phase Margin and Cross Over Frequencies From a Bode Plot
When the system gain is doubled the gain margin becomes?
Hence if gain of open loop system is doubled, then the gain margin will becomes half.
What is infinite gain margin?
Infinite Gain Margin
The gain margin of a system will be infinite if the phase of the loop gain never reaches -180° (i.e., if the Nyquist plot never crosses the real axis in the left half plane).
What is the gain on a root locus plot?
– The Root Locus Plot is a plot of the roots of the characteristic equation of the closed-loop system for all values of a system parameter, usually the gain; however, any other variable of the open- loop transfer function may be used.
What is the gain margin of system when the magnitude of the polar plot at the phase cross over is a?
Explanation: Gain margin of a polar plot passing through the critical point is zero.
What is gain crossover frequency?
Gain crossover frequency (ωgc): It is the frequency at which the magnitude of G(s) H(s) is unity. | G ( j ω ) H ( j ω ) | ω = ω g c = 1. Gain margin (GM): The gain margin of the system defines by how much the system gain can be increased so that the system moves on the edge of stability.
What is gain margin and phase margin in polar plot?
Gain margin (GM): The gain margin is the change in open-loop gain, expressed in decibels (dB), required at 180◦ of phase shift to make the closed-loop system unstable. Phase margin (PM): The phase margin is the change in open-loop phase shift, required at unity gain to make the closed-loop system unstable.
How does time delay affect phase margin?
– Time delay always decreases the phase margin of a system. – Gain crossover frequency is unaffected by a time delay.
How do you read a Bode plot?
Bode plots show the frequency response, that is, the changes in magnitude and phase as a function of frequency. This is done on two semi-log scale plots. The top plot is typically magnitude or “gain” in dB. The bottom plot is phase, most commonly in degrees.
Nyquist Analysis: Gain Margin and Phase Margin
Images related to the topicNyquist Analysis: Gain Margin and Phase Margin

What is phase margin in control system?
I. Gain margin is a factor by which the system gain can be increased to drive the system to the verse of instability. II. Phase margin is the additional phase lead at the gain cross over frequency to bring the system to verge of instability.
What is use of Bode plot?
Bode plots are a very useful way to represent the gain and phase of a system as a function of frequency. This is referred to as the frequency domain behavior of a system. This web page attempts to demystify the process.
Related searches
- Gain margin and phase margin in bode plot matlab
- gain margin and phase margin problems
- Phase margin
- how to find gain margin
- how to calculate gain margin and phase margin in matlab
- how to calculate phase margin and gain margin
- gain margin example
- gain margin formula
- how to show overshoot in matlab
- how to find gain margin from transfer function
- bode matlab
- how to find gain margin from bode plot in matlab
- how to find gain margin and phase margin in bode plot in matlab
- How to show overshoot in matlab
- phase margin
- how to find gain in matlab
- gain margin and phase margin in bode plot matlab
- phase crossover frequency calculator
- phase margin calculator online
Information related to the topic how to find gain margin in matlab
Here are the search results of the thread how to find gain margin in matlab from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic how to find gain margin in matlab. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.